Hello everyone! This video was recorded for the VMconf 22 Vulnerability Management conference, vmconf.pw. I will be talking about my open source project Scanvus. This project is already a year old and I use it almost every day.
Alternative video link (for Russia): https://vk.com/video-149273431_456239100
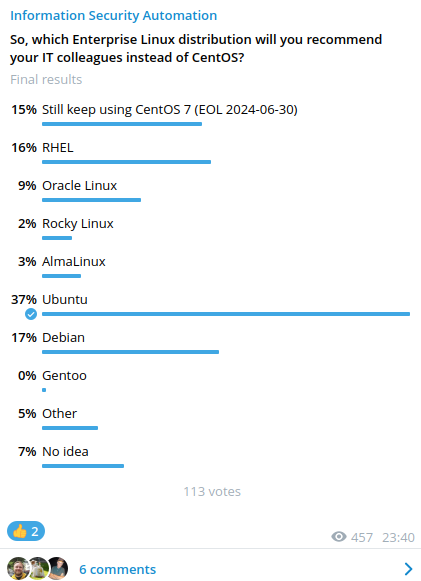
Scanvus (Simple Credentialed Authenticated Network VUlnerability Scanner) is a vulnerability scanner for Linux. Currently for Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, RedHat, Oracle Linux and Alpine distributions. But in general for any Linux distribution supported by the Vulners Linux API. The purpose of this utility is to get a list of packages and Linux distribution version from some source, make a request to an external vulnerabililty detection API (only Vulners Linux API is currently supported), and show the vulnerability report.
Scanvus can show vulnerabilities for
- localhost
- remote host via SSH
- docker image
- inventory file of a certain format
This utility greatly simplifies Linux infrastructure auditing. And besides, this is a project in which I can try to implement my ideas on vulnerability detection.
Example of output

For all targets the output is the same. It contains information about the target and the type of check. Then information about the OS version and the number of Linux packages. And finally, the actual information about vulnerabilities: how many vulnerabilities were found and the criticality levels of these vulnerabilities. The table shows the criticality level, bulletin ID, CVE list for the bulletin, and a comparison of the invulnerable fixed package version with the actual installed version.
This report is not the only way to present results. You can optionally export the results to JSON (OS inventory data, raw vulnerability data from Vulners Linux API or processed vulnerability data).
Continue reading