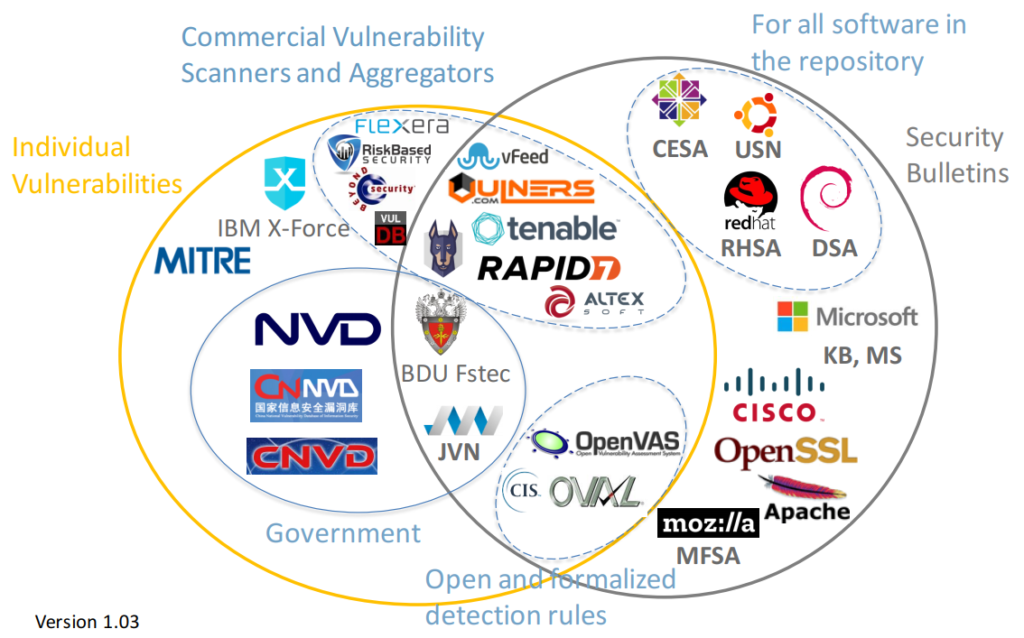
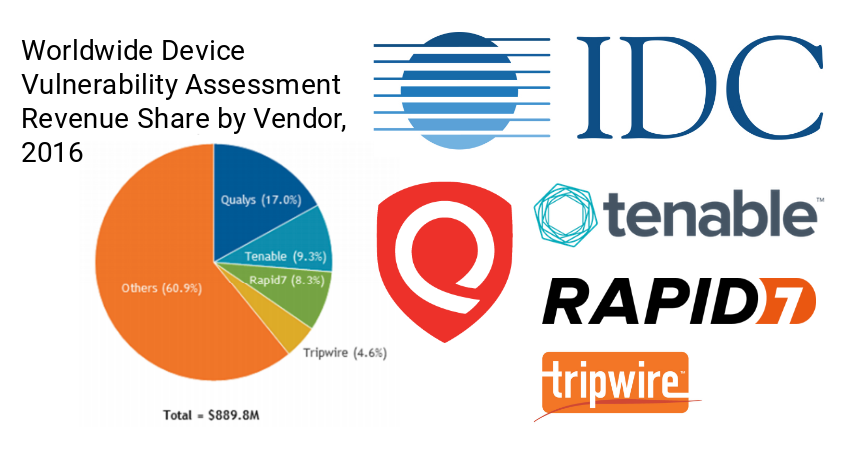
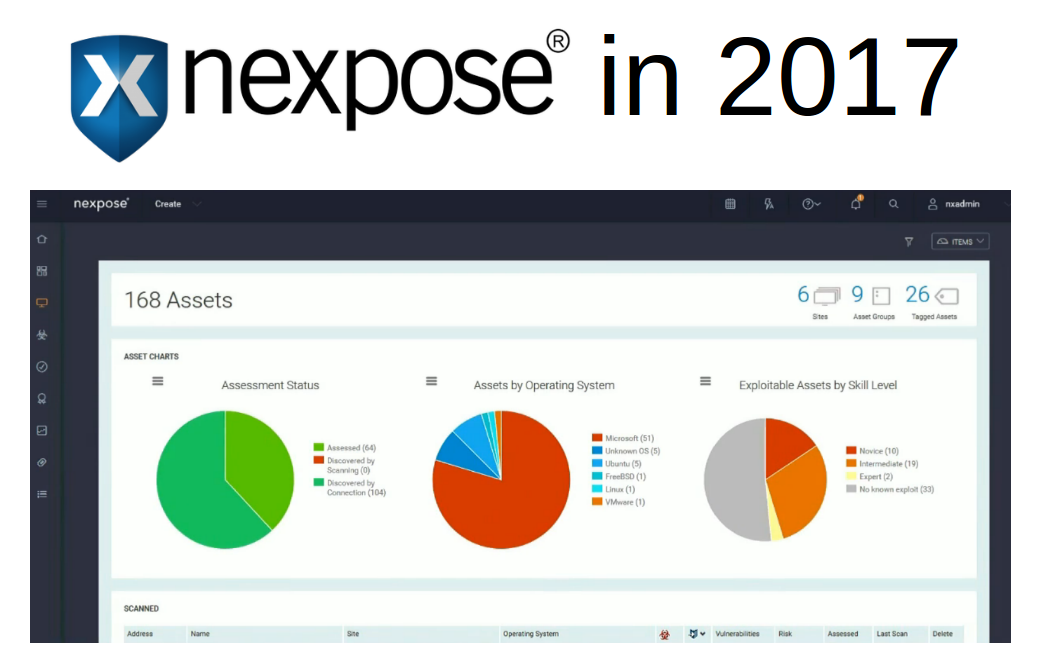
Hello everyone! This is the second episode of Vulnerability Management news and publications. In fact, this is a collection of my posts from the avleonovcom and avleonovrus telegram channels. Therefore, if you want to read them earlier, subscribe to these channels.
The main idea of this episode. Microsoft is a biased company. In fact, they should now be perceived as another US agency. Does this mean that we need to forget about Microsoft and stop tracking what they do? No, it doesn’t. They do a lot of interesting things that can at least be researched and copied. Does this mean that we need to stop using Microsoft products? In some locations (you know which ones) for sure, in some we can continue to use such products if it is reasonable, but it’s necessary to have a plan B. And this does not only apply to Microsoft. So, it’s time for a flexible approaches. Here we do it this way, there we do it differently. It seems that rather severe fragmentation of the IT market is a long-term trend and it’s necessary to adapt to it.
Alternative video link (for Russia): https://vk.com/video-149273431_456239097
What’s in this episode:
- Microsoft released a propaganda report, what does this mean for us?
- Microsoft released the Autopatch feature, is it a good idea to use it?
- Ridiculous Vulnerability: Hardcoded Password in Confluence Questions
- The new Nessus Expert and why it’s probably Tenable’s worst release
- Rapid7 Nexpose/InsightVM features added in Q2 2022: what’s good and what’s weird
- Palo Alto: Malicious scan 15 minutes after CVE is released. Oh really?
- 6 groups of vulnerabilities that are most often used in attacks, according to Palo Alto, and the end of IT globalization