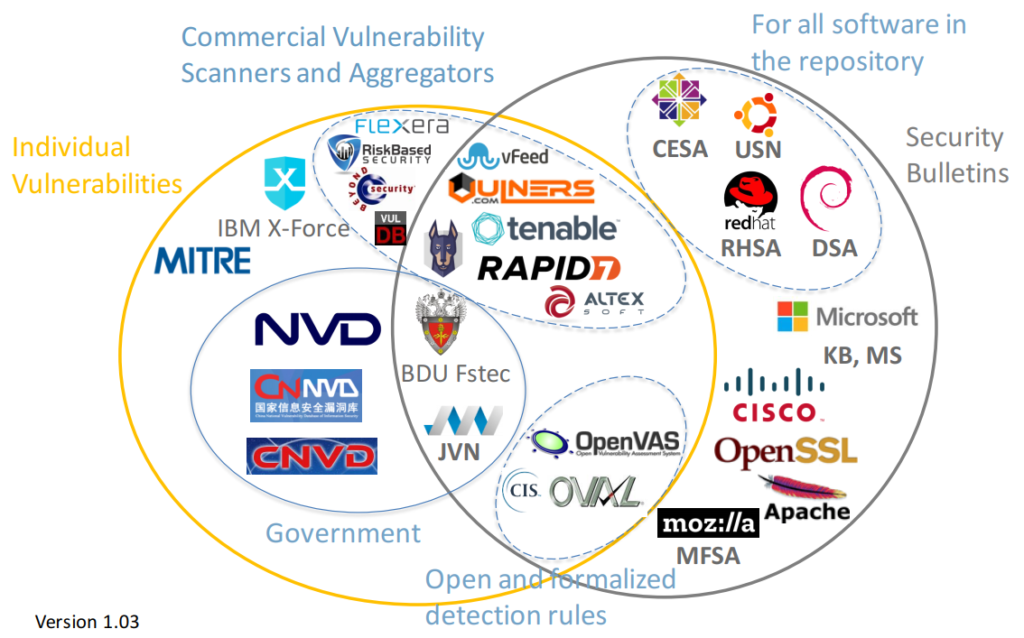
Hello everyone! As we saw in the last episode, the results of vulnerability detection for one host produced by two different APIs can vary greatly. Therefore, in order to find out the truth, it is necessary to understand what vulnerability data is provided by the Linux distribution vendor and how this data is structured.
Alternative video link (for Russia): https://vk.com/video-149273431_456239114
Why is it important to do this? Because using data from a Linux distribution vendor, we can ask vulnerability detection API vendors questions: why are you detecting in a different way than described in this data? And then we will understand what caused the difference. And we will either adjust the API for vulnerability detection, or we will adjust the content of the Linux distribution vendor. Either way, it will be a success! In any case, the transparency of the vulnerability detection process will increase.
Last time we looked at vulnerabilities for Debian host and Debian Docker base image. So let’s continue with Debian. In particular, with the official Debian OVAL (Open Vulnerability and Assessment Language) content.
Debian OVAL content can be downloaded from the https://debian.org/security/oval/ website. For Debian 11.6 it will be https://debian.org/security/oval/oval-definitions-bullseye.xml (~48M).
Continue reading