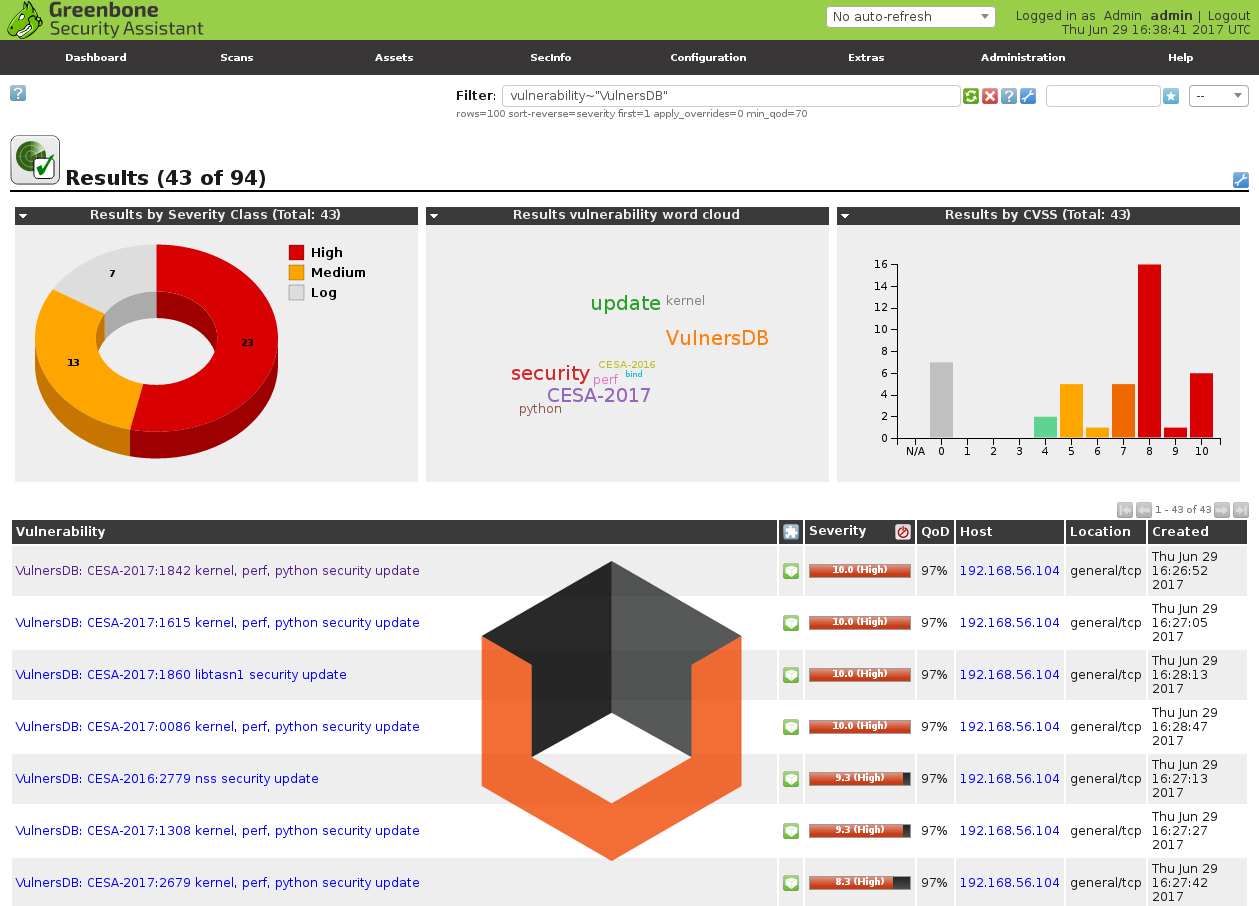
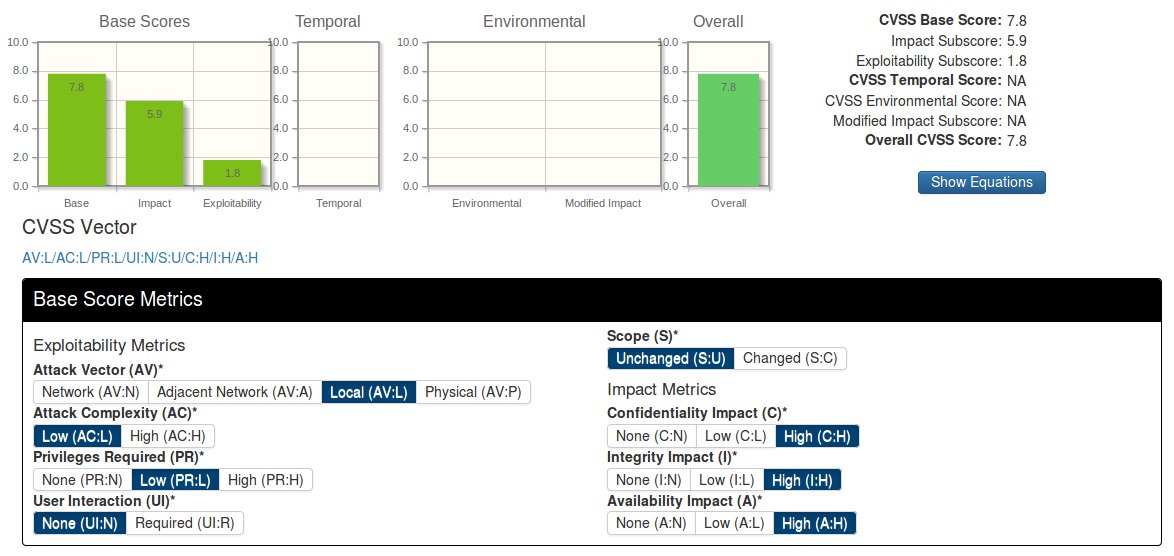
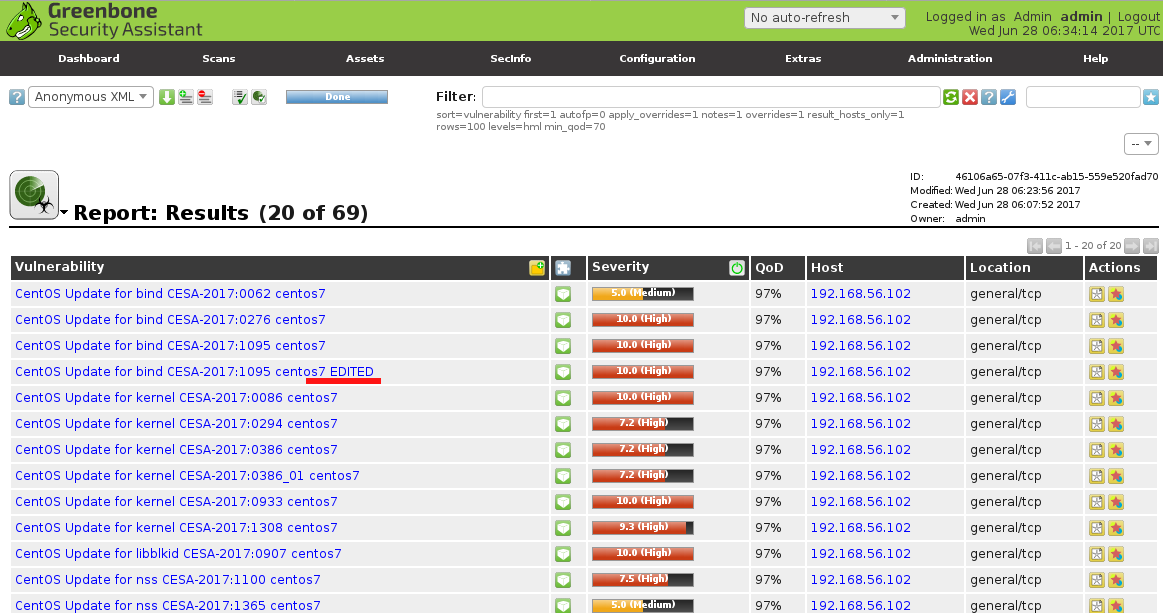
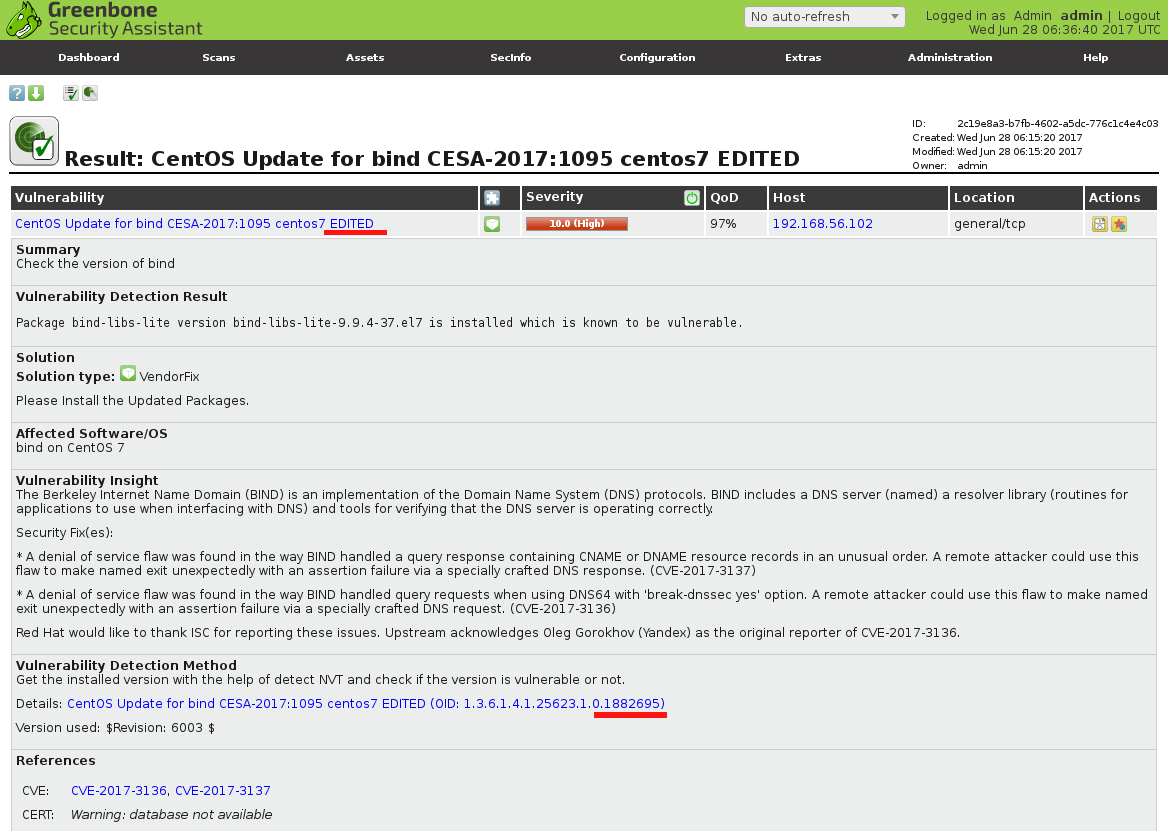
What publicly available Vulnerability Databases do we have? Well, I can only say that there are a lot of them and they are pretty different. Here I make an attempt to classify them.
It’s quite an ungrateful task. No matter how hard you try, the final result will be rather inaccurate and incomplete. I am sure someone will be complaining. But this is how I see it. 😉 If you want to add or change something feel free to make a comment bellow or email me@avleonov.com.
The main classifier, which I came up with:
- There are individual vulnerability databases in which one identifier means one vulnerability. They try to cover all existing vulnerabilities.
- And others are security bulletins. They cover vulnerabilities in a particular product or products. And they usually based on on patches. One patch may cover multiple vulnerabilities.
I made this diagram with some Vulnerability Databases. Note that I wanted to stay focused, so there are no exploit DBs, CERTs, lists of vulnerabilities detected by some researchers (CISCO Talos, PT Research, etc.), Media and Bug Bounty sites.
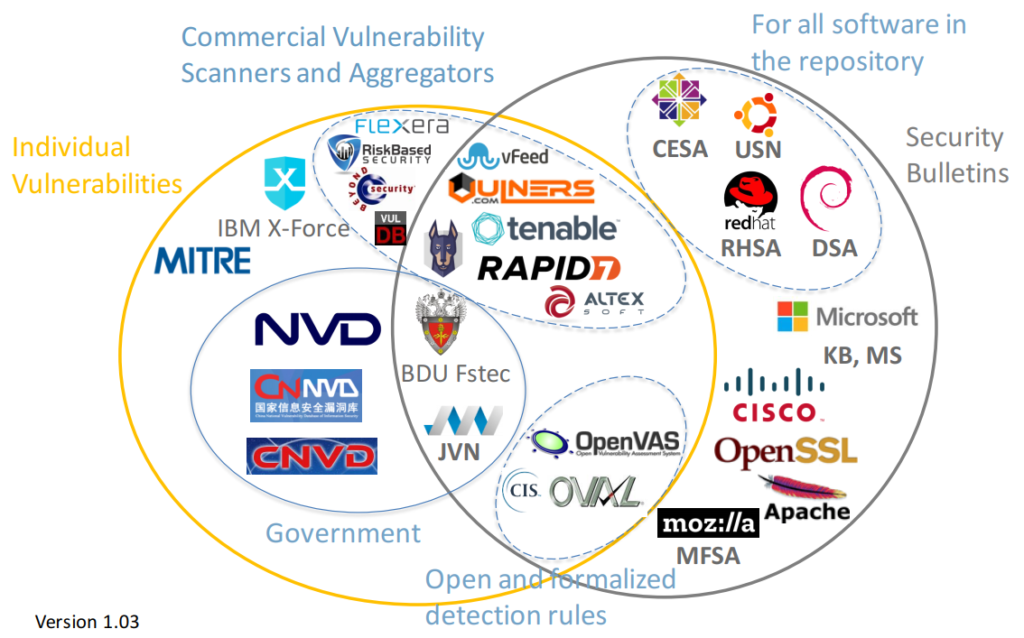
For these databases the descriptions of vulnerabilities are publicly available on the site (in html interface or downloadable data feed), or exist in a form of paid Vulnerability Intelligence service (for example, Flexera).
On one side there are databases of individual vulnerabilities, the most important is National Vulnerability Database. There are also Chinese, Japanese bases that can be derived from NVD or not.
On the other side we have security bulletins, for example RedHat Security Advisories.
And in the middle we have a Vulnerability Databases, for which it is not critical whether they have duplicated vulnerability IDs or not.