I have finalized the list of trending vulnerabilities for 2024 according to Positive Technologies. Last year, 74 vulnerabilities were classified as trending (to compare the scale, just over 40,000 were added to NVD in 2024).
All trending vulnerabilities are found in Western commercial products and open source projects. This year, the vulnerabilities of domestic Russian products did not reach the level of criticality required to classify them as trending.
For 55 of all trending vulnerabilities there are currently signs of exploitation in attacks, for 17 there are public exploits (but no signs of exploitation) and for the remaining 2 there is only a possibility of future exploitation.
Vulnerabilities were often added to trending ones before signs of exploitation in the wild appeared. For example, the remote code execution vulnerability in VMware vCenter (CVE-2024-38812) was added to the list of trending vulnerabilities on September 20, 3 days after the vendor’s security bulletin appeared. There were no signs of exploitation in the wild or public exploit for this vulnerability. Signs of exploitation appeared only 2 months later, on November 18.
Most of the vulnerabilities in the trending list are of the following types: Remote Code or Command Execution (24) and Elevation of Privilege (21).
4 vulnerabilities in Barracuda Email Security Gateway (CVE-2023-2868), MOVEit Transfer (CVE-2023-34362), papercut (CVE-2023-27350) and SugarCRM (CVE-2023-22952) were added in early January 2024. These vulnerabilities were massively exploited in the West in 2023, and attacks using these vulnerabilities could also tangentially affect those domestic Russian organizations where these products had not yet been taken out of service. The rest of the vulnerabilities became trending in 2024.
34 trending vulnerabilities affect Microsoft products (45%).
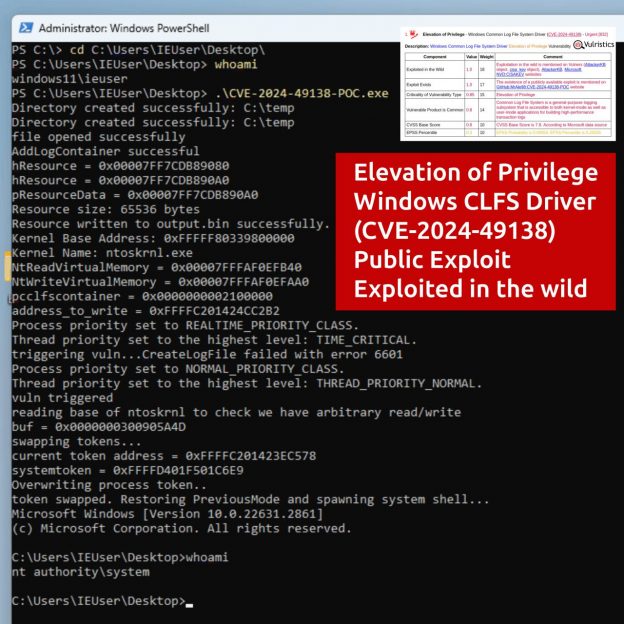
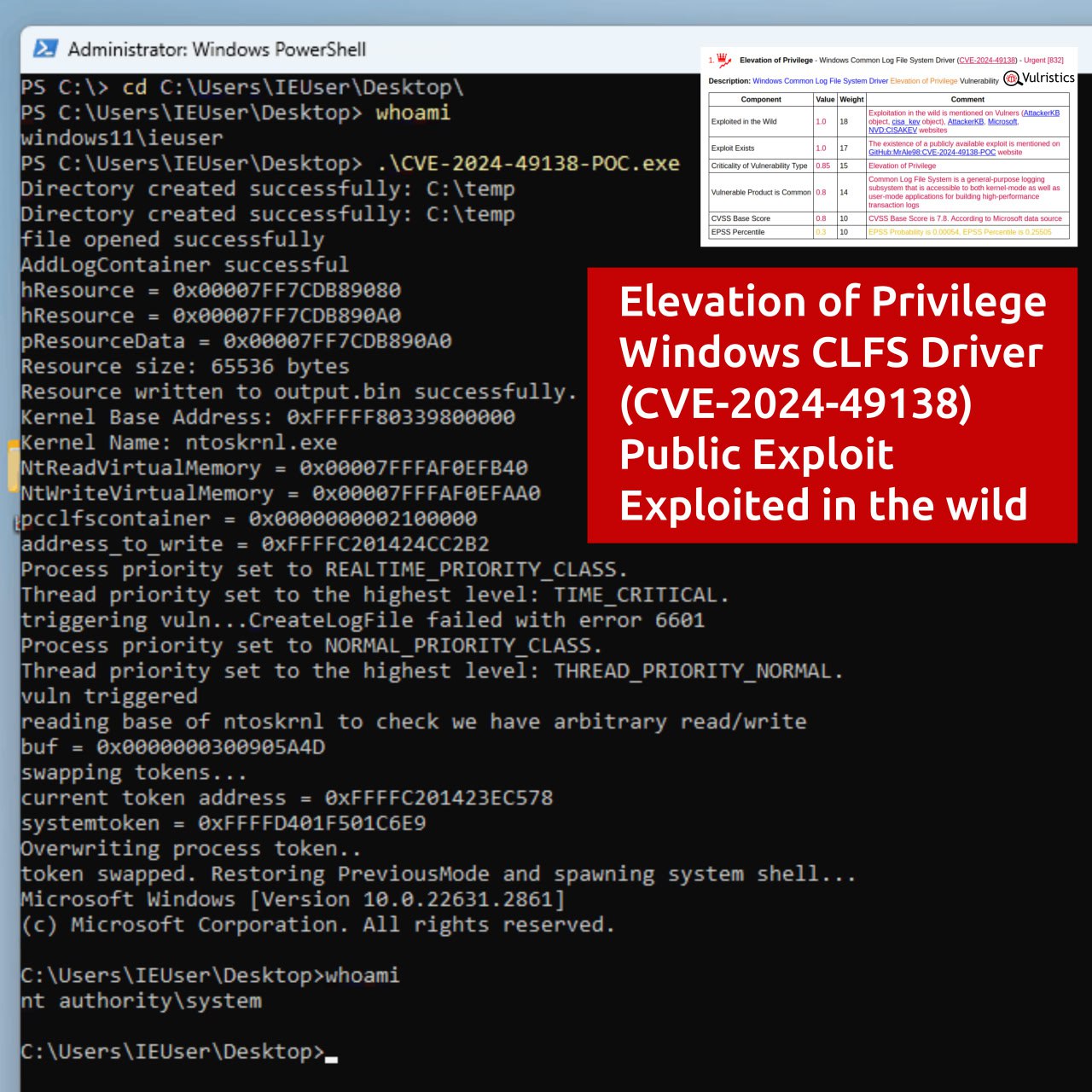
🔹 17 of them are Elevation of Privilege vulnerabilities in the Windows kernel and standard components.
🔹 1 Remote Code Execution vulnerability in Windows Remote Desktop Licensing Service (CVE-2024-38077).
2 trending Elevation of Privilege vulnerabilities affect Linux systems: one in nftables (CVE-2024-1086), and the second in needrestart (CVE-2024-48990).
Other groups of vulnerabilities
🔻 Phishing attacks: 19 (Windows components, Outlook, Exchange, Ghostscript, Roundcube)
🔻 Network security and entry points: 13 (Palo Alto, Fortinet, Juniper, Ivanti, Check Point, Zyxel)
🔻 Virtual infrastructure and backups: 7 (VMware, Veeam, Acronis)
🔻 Software development: 6 (GitLab, TeamCity, Jenkins, PHP, Fluent Bit, Apache Struts)
🔻 Collaboration tools: 3 (Atlassian Confluence, XWiki)
🔻 CMS WordPress plugins: 3 (LiteSpeed Cache, The Events Calendar, Hunk Companion)
🗒 Full Vulristics report
🟥 Article on the official website “Vulnerable software and hardware vs. security researchers” (rus)
На русском