Hello everyone! This episode will be about Microsoft Patch Tuesday for July 2023, including vulnerabilities that were added between June and July Patch Tuesdays.
Alternative video link (for Russia): https://vk.com/video-149273431_456239131
As usual, I use my open source Vulristics project to analyse and prioritize vulnerabilities.
Vulristics improvements
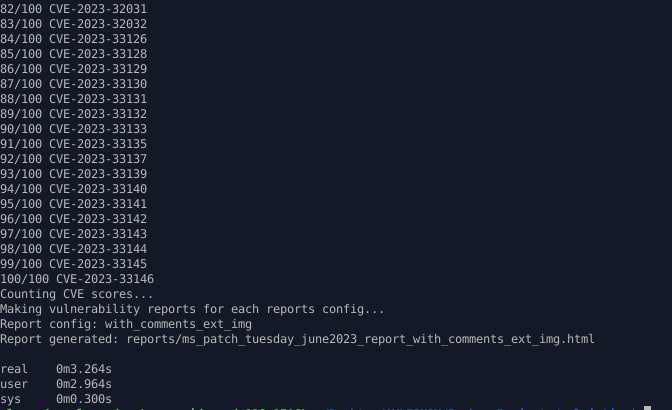
I optimized the detection of the vulnerable product and the type of vulnerability based on the description. Now processing already downloaded data (with option --rewrite-flag "False") takes a few seconds. For example, only ~3 seconds for 100 MS Patch Tuesday vulnerabilities . It used to take a few minutes.
What I’ve done:
- For Microsoft generated descriptions, e.g. “Microsoft Excel Remote Code Execution Vulnerability”, vulnerability type and product are now directly parsed out of the description, keyword search is not performed.
- I rewrote the generic keyword search based on products.json. I have reduced the use of heavy functions without sacrificing the quality of the detections.