


I generated a Vulristics report on the April Linux Patch Wednesday. Over the past month, Linux vendors have begun releasing patches for a record number of vulnerabilities – 348. There are signs of exploitation in the wild for 7 vulnerabilities (data on incidents from the FSTEC BDU). Another 165 have a link to an exploit or a sign of the existence of a public/private exploit.
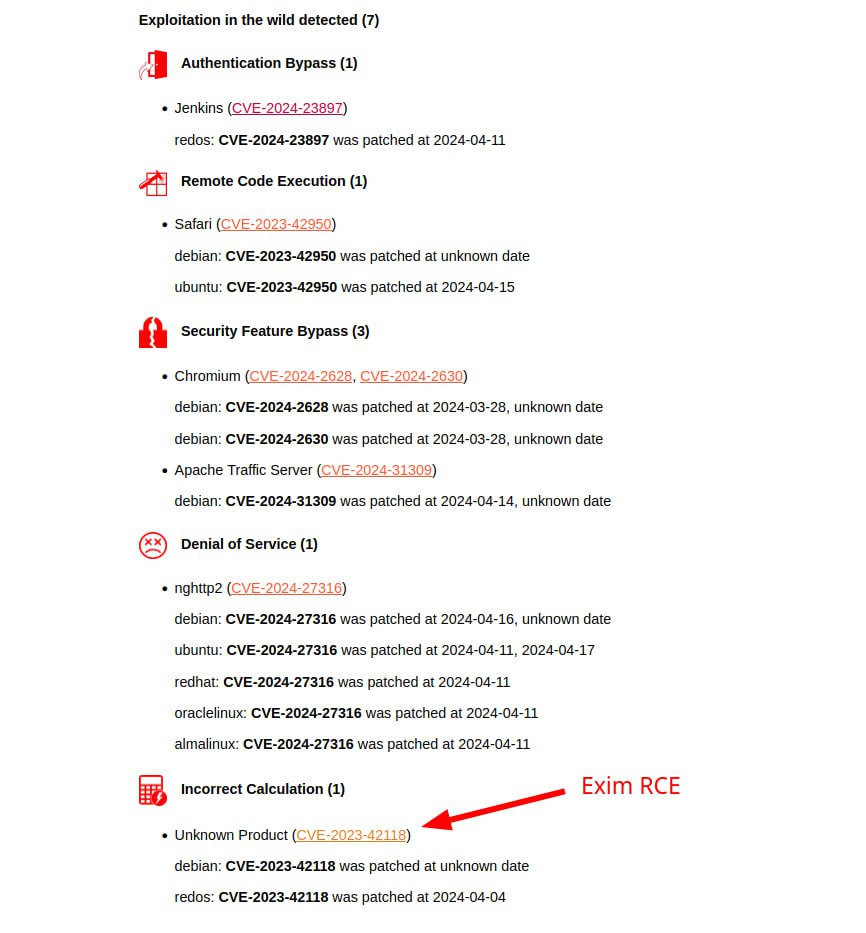
Let’s start with 7 vulnerabilities with signs of exploitation in the wild and exploits:
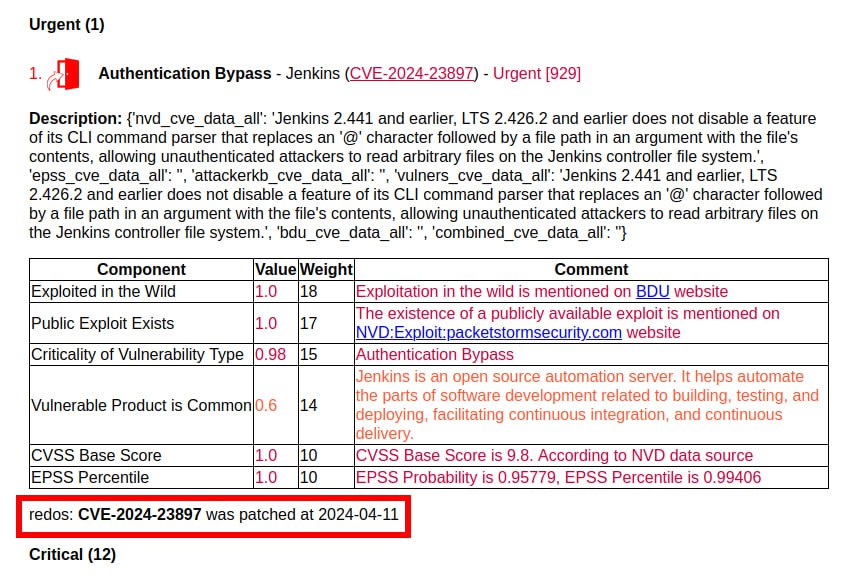
🔻 The trending January vulnerability Authentication Bypass – Jenkins (CVE-2024-23897) unexpectedly appeared in the TOP. As far as I understand, Linux distributions usually do not include Jenkins packages in the official repositories and, accordingly, do not add Jenkins vulnerability detection rules to their OVAL content. Unlike the Russian Linux distribution RedOS. Therefore, RedOS has the earliest fix timestamp for this vulnerability.
🔻 2 RCE vulnerabilities. The most interesting of them is Remote Code Execution – Exim (CVE-2023-42118). When generating the report, I deliberately did not take into account the vulnerability description and product names from the BDU database (flags –bdu-use-product-names-flag, –bdu-use-vulnerability-descriptions-flag set to False). Otherwise, the report would be partly in English and partly in Russian. But it turned out that so far only BDU has an adequate description of this vulnerability. 🤷♂️ You need to take a closer look at this vulnerability because Exim is a fairly popular mail server. The second RCE vulnerability is in the web browser, Remote Code Execution – Safari (CVE-2023-42950).
🔻2 DoS vulnerabilities. Denial of Service – nghttp2/Apache HTTP Server (CVE-2024-27316) and Denial of Service – Apache Traffic Server (CVE-2024-31309). The second is classified in the report as Security Feature Bypass, but this is due to incorrect CWE in NVD (CWE-20 – Improper Input Validation)
🔻 2 browser vulnerabilities Security Feature Bypass – Chromium (CVE-2024-2628, CVE-2024-2630)
Among the vulnerabilities for which there are only signs of the existence of exploits so far, you can pay attention to the following:
🔸 A large number of RCE vulnerabilities (71). Most of them are in the gtkwave product. This is a viewer for VCD (Value Change Dump) files, which are typically created by digital circuit simulators. Also, the Remote Code Execution – Cacti (CVE-2023-49084, CVE-2023-49085) vulnerabilities look dangerous. Cacti is a solution for monitoring servers and network devices.
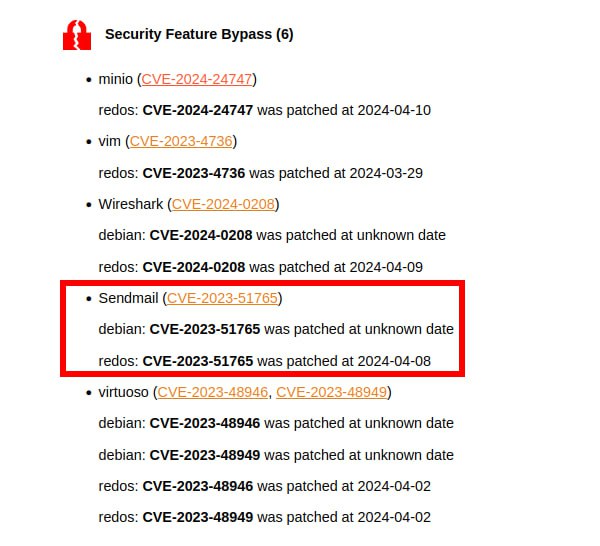
🔸 Security Feature Bypass – Sendmail (CVE-2023-51765). Allows an attacker to inject email messages with a spoofed MAIL FROM address.
🔸 A pack of Cross Site Scripting vulnerabilities in MediaWiki, Cacti, Grafana, Nextcloud.
There is a lot to explore this time. 🤩
🗒 April Linux Patch Wednesday
На русском











