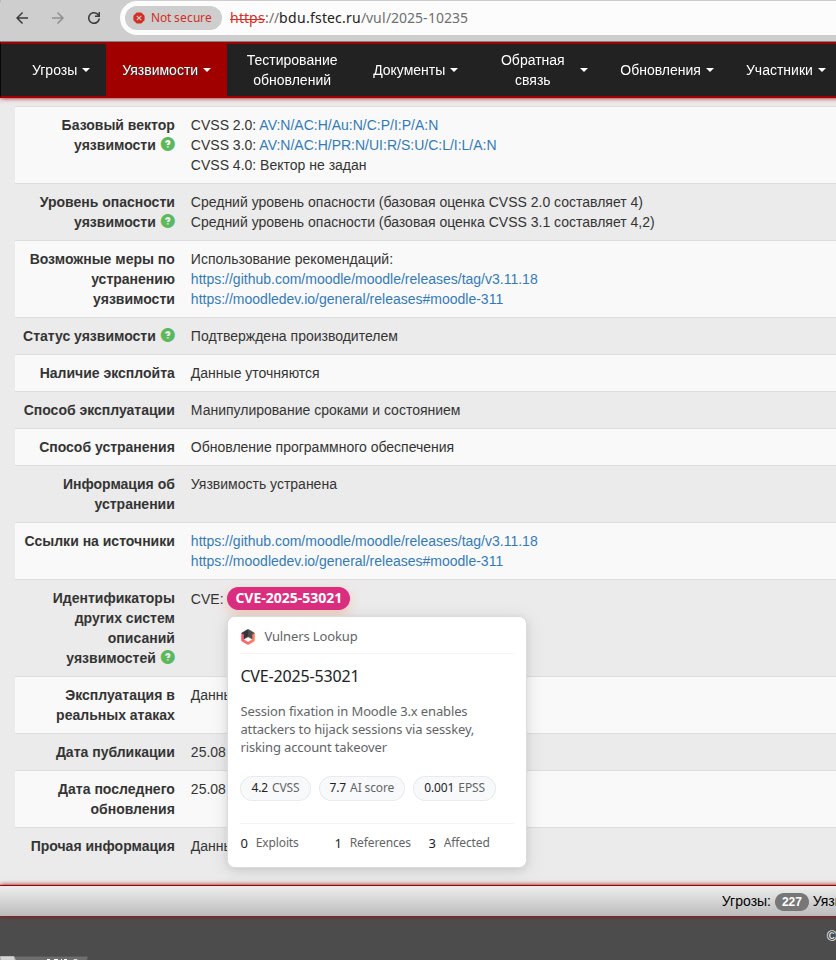
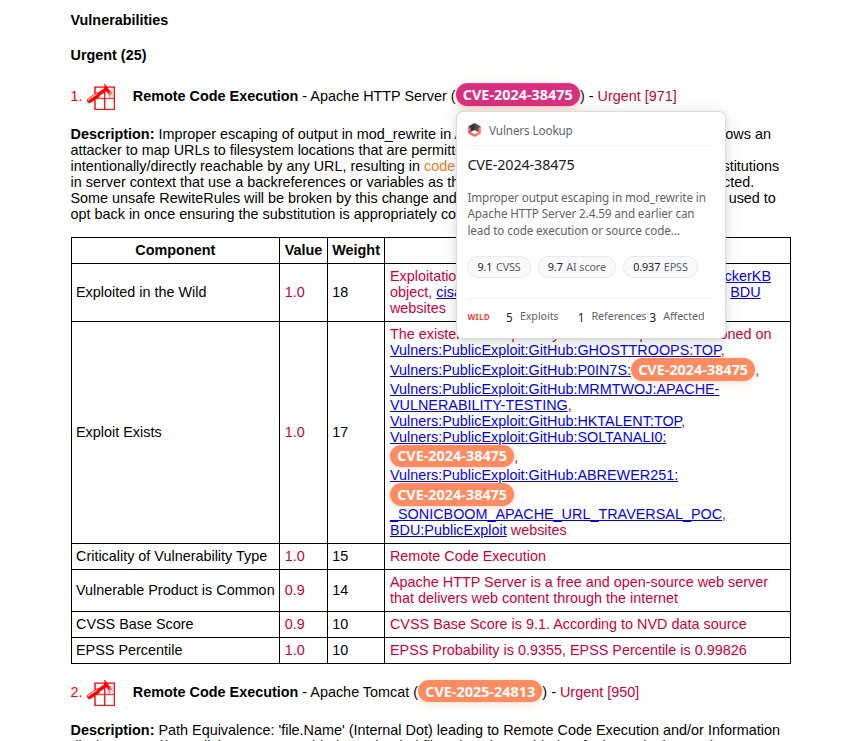
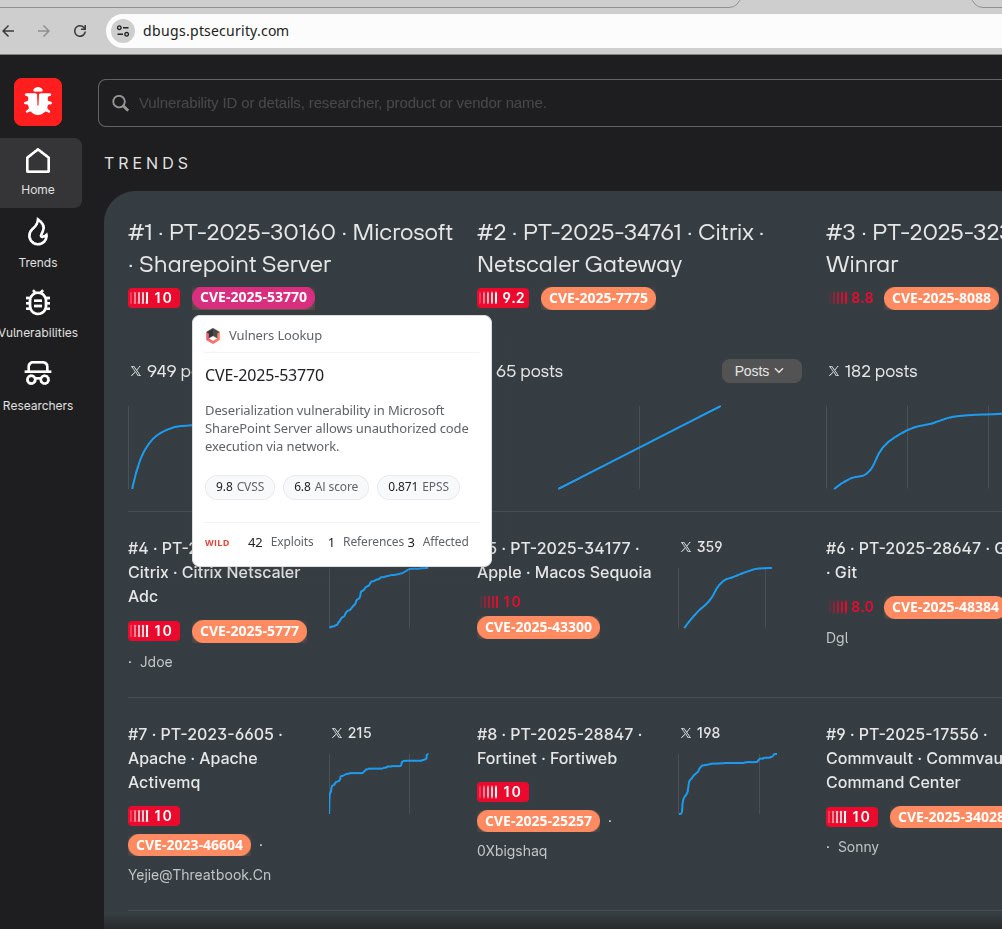
September Linux Patch Wednesday. In September, Linux vendors began addressing 748 vulnerabilities, slightly fewer than in August. Of these, 552 are in the Linux Kernel. The share of Linux Kernel vulnerabilities is growing! One vulnerability shows signs of being actively exploited (CISA KEV):
🔻 MemCor – Chromium (CVE-2025-10585). Public exploits are available.
For 63 (❗️) vulnerabilities, public exploits are available or there are signs they exist. Notable ones include:
🔸 RCE – CivetWeb (CVE-2025-55763), ImageMagick (CVE-2025-55298), Asterisk (CVE-2025-49832), libbiosig (CVE-2025-46411 and 22 other CVEs), sail (CVE-2025-32468 and 7 other CVEs)
🔸 AuthBypass – OAuth2 Proxy (CVE-2025-54576), CUPS (CVE-2025-58060)
🔸 EoP – UDisks (CVE-2025-8067)
🔸 SQLi – Django (CVE-2025-57833)
🔸 SFB – CUPS (CVE-2025-58364)