It’s the third part of our talk with Daniil Svetlov at his radio show “Safe Environment” recorded 29.03.2017. In this part we talk about Vulnerability Prioritization and Detection:
- Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS)
- Environmental factor
- Manual and automated vulnerability detection
- Unauthenticated and authenticated scanning
- Why vulnerability scanners are so expensive and why the can’t detect everything

Video with manually transcribed Russian/English subtitles:
Prioritization
– Here also the question how to prioritize vulnerabilities properly. Because if you have, as you said, two Linux servers and 20 workstations running Windows, then in principle, you may not need to do prioritization. But if you have fifteen hundred servers: some of them are on perimeter, some are in your DMZ, some are in the internal network. It is still necessary, probably, to understand correctly which vulnerabilities and where should be patched in in the first place.
Yes, this is absolutely true and it’s a very good question. How to prioritize?
Common Vulnerability Scoring System
A natural way. If we look at vulnerabilities with a CVE identifier, for them in the US National Vulnerability Database we can find CVSS Base Score. It is an assessment of vulnerability criticality level.
How is it calculated?
Some person fills the questionnaire: can it be remotely exploited – no, is there public exploit – no, etc.
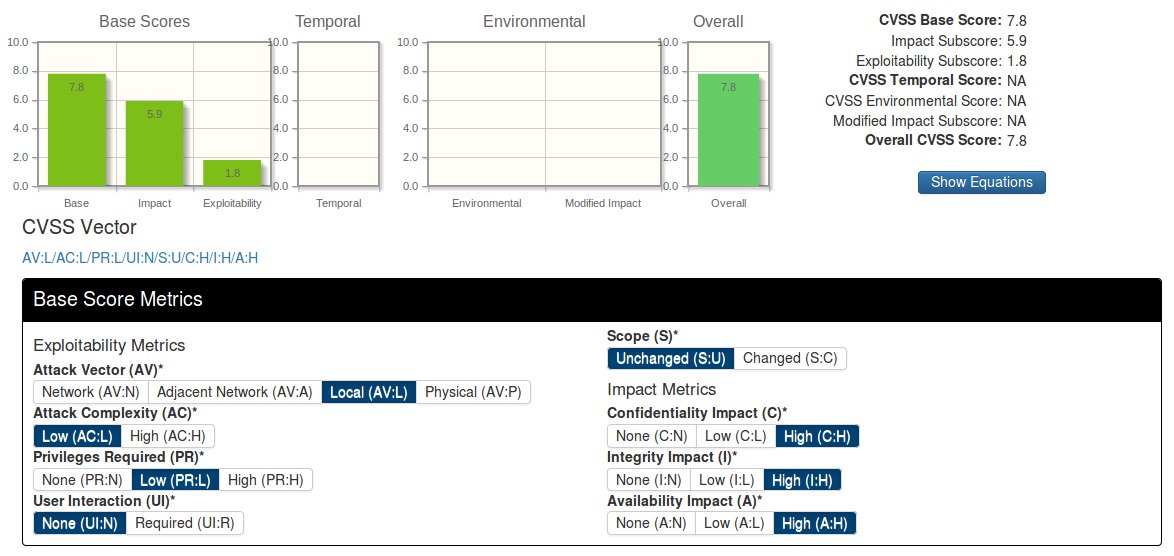
The result is a CVSS vector – this is a line in which you can see the main characteristics of this vulnerability and CVSS Base score is the score from 0 to 10 depending on criticality.
This is a natural way of prioritization. But sometimes this method does not give very good results.