New Advanced Dynamic Scan Policy Template in Nessus 8. According to Nessus 8.1.0 release notes, Tenable finally solved the problem with Mixed Plugin groups. At least partially. I will briefly describe the problem. Let’s say we found out that some Nessus plugins crash our target systems. This happens rarely, but it happens. So, we decided to disable these plugins in the scan policy:
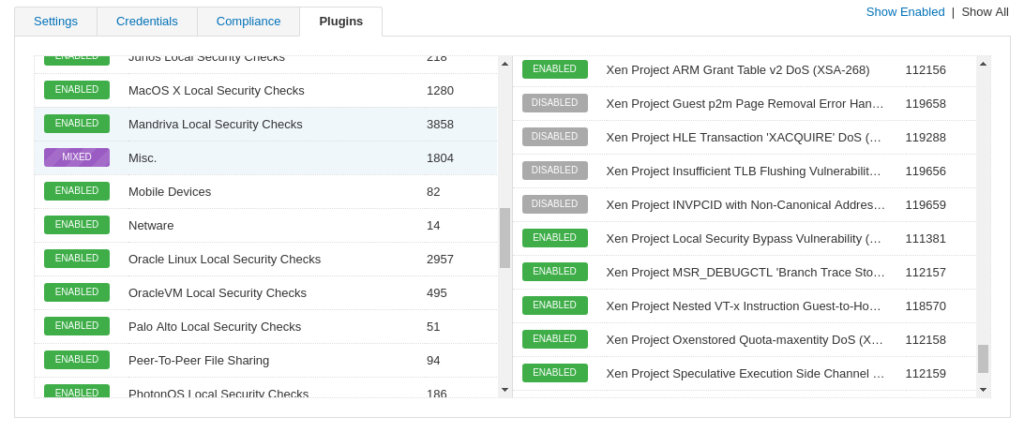
Ok, problem is solved. But here is the question: what will happen with the new NASL plugins that will be added by Tenable in the same group, for example Misc.?
The answer is quite sad: Nessus doesn’t know if they should enabled of disabled, so they will be disabled in the scan policy by default. And this can lead to some False-Negatives. For example, on this screenshot you can see a fresh plugin “Xen Project Guest p2m Page Removal Error Handling DoS (XSA-277)” Published: December 13, 2018 was automatically disabled.
Previously, it was necessary to monitor this situation and add these plugins to Enabled manually or via API. But now with a new Dynamic Scan Policy template, this might be changed.